Russian Alphabet
The Russian alphabet consists of 33 letters: 10 vowels (а, е, ё, и, о, у, ы, э, ю, я), 21 consonants and 2 signs (hard and soft) that are not pronounced. The Russian alphabet uses the Cyrillic script.
Some letters of the Russian alphabet look like and sound similar to the letters of the Latin alphabet. But there are also significant differences. The phonetic transcription helps pronounce a word more or less correctly. It might be difficult, though, to get exactly the right sound just reading the transcription. It is better to learn the Russian alphabet using audio samples.
Note:
- In Russian, the pronunciation of vowels is affected by word stress. Stressed vowels are pronounced clearly and distinctly whereas unstressed vowels are shorter and weaker (reduced). That is why the stressed vowels are marked red in the table below. There is no mark in one syllable words.
- The symbol [j] (a superscript j) marks soft (palatalized) consonants (Unicode U+02B2 of the International Phonetic Alphabet)
| Letter + Handwriting |
Name of the letter |
Transcription + Pronunciation | Pronunciation Samples (red = stressed) |
||
А а 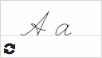 |
a | [a] (open and clear if stressed) [a] / [i] (reduced if unstressed) |
как [á] = how какой [a] = which, what часы [i] = clock, watch |
||
Б б 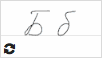 |
бэ [be] |
[b] (voiced) [bj] (voiced soft) [p] (voiceless) [pj] (voiceless soft) |
быть [b] = be бить [bj] = beat клуб [p] = club голубь [pj] = pigeon |
||
В в  |
вэ [ve] |
[v] (voiced) [vj] (voiced soft) [f] (voiceless) [fj] (voiceless soft) |
вы [v] = you виза [vj] = visa все [f] = all кровь [fj] = blood |
||
Г г  |
гэ [ge] |
[g] (voiced) [gj] (voiced soft) [k] (voiceless) |
год [g] = year гимн [gj] = hymn слог [k] = syllable |
||
Д д 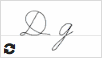 |
дэ [de] |
[d] (voiced) [dj] (voiced soft) [t] (voiceless) [tj] (voiceless soft) |
да [d] = yes день [dj] = day вход [t] = entrance будь [tj] = be (Imperativ 1st Person Sing.) |
||
Е е  |
е [ye] |
[ye] as in yet (in the initial position, after vowels and after ь and ъ) [e] / [i] / [ɨ] (after consonants, regardless of stress) Note: - the preceding consonant is soft |
ехать [ye] = go, drive пьеса [ye] = theater play диета [ye] = diet нет [nje] = no немного [nji] = a little, a few желать [ɨ] = wish |
||
Ё ё  |
ё [yo] |
[yo] as in your (in the initial position, after vowels and after ь and ъ) [o] (after consonants) Note: - the preceding consonant is soft; - ё is always stressed; - it is often written without dots on top |
ёлка [yo] = fir tree даёт [yo] = he/she gives пьёт [yo] = he/she drinks всё [o] = everything |
||
Ж ж 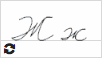 |
жэ [zhe] |
[zh] voiced as in leisure [sh] voiceless as in sure Note: - always hard |
жена [zh] = wife муж [sh] = husband |
||
З з  |
зэ [ze] |
[z] (voiced as in zone) [zj] (voiced soft) [s] (voiceless as is sown) [sj] (voiceless soft) |
завтра [z] = tomorrow зима [zj] = winter близко [s] = near мазь [sj] = ointment |
||
И и  |
и [i] |
[i] / [ee] (as in tee) [ɨ] (after ж, ш, ц) Note: - the pronunciation is more or less the same in stressed and unstressed syllables; - the preceding consonant is soft |
алфавит [i] = alphabet машина [ɨ] = car |
||
Й й  |
и краткое [i krátkaye] short I |
[y] as in toy Note: - always soft and voiced |
мой = my | ||
К к 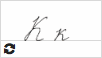 |
ка [ka] |
[k] (voiceless) [kj] (voiceless soft) Note: - In Russian, it is not aspirated like the K in skip |
кот [k] = cat кит [kj] = whale |
||
Л л  |
эль [elj] |
[l] (voiced) [lj] (voiced soft, like in the French name Michelle) |
луна [l] = moon люди [lj] = people |
||
М м  |
эм [em] |
[m] (voiced) [mj] (voiced soft) |
сам [m] = myself, himself семь [mj] = seven |
||
Н н  |
эн [en] |
[n] (voiced) [nj] (voiced soft) |
она [n] = she они [nj] = they |
||
О о 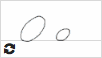 |
о [o] |
[o] (when stressed it is a clear O-sound as in or) [a] (reduced when unstressed) |
тот [o] = that (m) этот [a] = this (m) |
||
П п 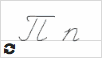 |
пэ [pe] |
[p] (voiceless) [pj] (voiceless soft) Note: - In Russian, it is not aspirated like the P in speak |
пока [p] = Bye пить [pj] = drink |
||
Р р 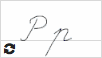 |
эр [er] |
[r] (voiced) [rj] (voiced soft) Note: - The Russian R is rolled with the tip of the tongue |
рука [r] = arm, hand рюмка [rj] = small liqueur glass |
||
С с  |
эс [es] |
[s] (voiceless) [sj] (voiceless soft) |
сад [s] = garden сидеть [sj] = sit |
||
Т т  |
тэ [te] |
[t] (voiceless) [tj] (voiceless soft) Note: - In Russian, it is not aspirated like the T in stick |
тогда [t] = then тётя [tj] = aunt |
||
У у 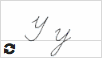 |
у [u] |
[u] / [oo] Note: - the pronunciation is more or less the same in stressed and unstressed syllables (except for some special cases) |
русский [u] = Russian | ||
Ф ф 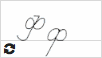 |
эф [ef] |
[f] (voiceless) [fj] (voiceless soft) |
фото [f] = photo фильм [fj] = film |
||
Х х 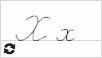 |
ха [ha] / [kha] |
[h] / [kh](voiceless, similar to Lochness) [hj] / [khj] (voiceless soft) |
хохотать [kh] = laugh loud хихикать [khj] = chuckle |
||
Ц ц  |
цэ [tse] |
[ts] (similar to tsar) Note: - always voiceless and hard |
немецкий [ts] = German | ||
Ч ч  |
че [che] |
[ch] / [tch] (as in cheers or Tchaikovsky) Note: - always voiceless and soft |
учить [ch] = learn, teach | ||
Ш ш 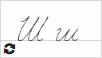 |
ша [sha] |
[sh] (as in shop) Note: - always voiceless and hard |
слушать [sh] = hear | ||
Щ щ 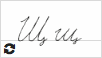 |
ща [shsha] |
[shsh] (similar to fresh shots) Note: - sometimes it is transcribed as [shch] which might be confusing as the Russian letter Щ is pronounced more like the long Ш [shsh] and not like the combination auf Ш and Ч [shch]; - always voiceless and soft |
ещё [shsh] = still, yet | ||
ъ 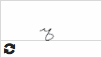 |
твёрдый знак [tvjórdɨj znak] hard sign |
- the hard sign is not pronounced; - it appears only between a consonant and the vowels -е, -ё, -ю, -я (with the exception of some loanwords); - the preceding consonant is hard; - the succeeding vowels are pronounced with the distinct initial Y-sound (ye, yo, yu, ya). |
съесть [sye] (with ъ) = eat up сесть [sje] (without ъ) = sit down |
||
ы  |
ы [ɨ] |
[ɨ] Note: - Ы is a retracted (half backed) variety of И [i] pronounced with the root of the tongue blocking the throat; - the pronunciation is more or less the same in stressed and unstressed syllables |
ты [ɨ] = you | ||
ь 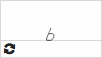 |
мягкий знак [mjákhjkjɪj znak] soft sign |
[j] - the soft sign is not pronounced; - the preceding consonant is soft; - the succeeding vowels -е, -ё, -и, -ю, -я are pronounced with the distinct initial Y-sound (ye, yo, yi, yu, ya). |
есть [tj] (with ь) = eat ест [t] (without ь) = he/she eats семья [mja] (with ь) = family семя [mja] (without ь) = seed |
||
Э э  |
э [e] |
[e] (similar to set or rap) Note: - the pronunciation is more or less the same in stressed and unstressed syllables; - usually appears in the initial position or after vowels |
это [e] = this, that, it поэтому [e] = that's why |
||
Ю ю 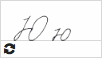 |
ю [yu] |
[yu] / [yoo] (in the initial position, after ъ, ь or after vowels) [u] (after consonants) Note: - the preceding consonant is soft; - the pronunciation is more or less the same in stressed and unstressed syllables. |
юмор [yu] = humor ночью [yu] = at / by night союз [yu] = union любовь [lju] = love |
||
Я я 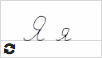 |
я [ya] |
[ya] (in the initial position, after ъ, ь or after vowels) [yi] or a combination of [yi] and [ya] (if unstressed) [a] / [i] (after consonants, regardless of the stress) Note: - the preceding consonant is soft |
ясно [ya] = clear друзья [ya] = friends Россия [ya] = Russia язык [yɨ] = language, tongue имя [mja] = name |
About the Cyrillic and Russian Alphabet
In the middle of the 9th century, the Byzantine philosopher Cyril together with his brother Methodius created the Glagolic alphabet. It was one of the first Slavic alphabets and was used to write down religious texts. The Cyrillic alphabet developed from the Glagolic and Greek scripts and was named after Cyril.
The brothers Cyril and Methodius were declared saints both by the Catholic and the Orthodox Church. In Russia, the saints’ feast day on May 24 is celebrated as Slavonic Literature and Culture Day (Russian: День славянской письменности и культуры).
Russian is written in the Cyrillic script. The early Russian alphabet consisted of 43 letters. With time, the number was reduced to 33 eliminating some letter and introducing new ones. The last reform of Russian orthography took place in 1917/1918.
In Russian, the alphabet is also called азбука [ásbuka]. This word is derived from old names of the letters A = азъ [as] and Б = буки [búkji]. So the word азбука corresponds to the English ABC.
More to learn Russian
Russian Letters and Pronunciation
Russian Verb Trainer App
Basic words and phrases in Russian
Russian Vocabulary Lists by Topic